Make It Count
When queries go parallel, you want them to be fast. Sometimes they are, and it’s great.
Other times they’re slow, and you end up staring helplessly at a repartition streams operator.
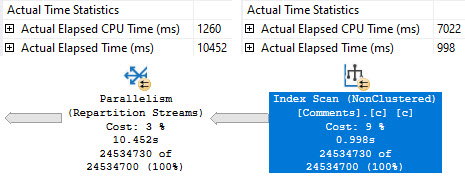
Sometimes you can reduce the problem with higher DOP hints, or better indexing, but overall it’s a crappy situation.
Snap To
Let’s admire a couple familiar looking queries, because that’s been working really well for us so far.
WITH Comments AS
(
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY
c.UserId
ORDER BY
c.CreationDate) AS n
FROM dbo.Comments AS c
)
SELECT *
FROM Comments AS c
WHERE c.n = 0
OPTION(USE HINT('QUERY_OPTIMIZER_COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL_140'));
WITH Comments AS
(
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY
c.UserId
ORDER BY
c.CreationDate) AS n
FROM dbo.Comments AS c
)
SELECT *
FROM Comments AS c
WHERE c.n = 0
OPTION(USE HINT('QUERY_OPTIMIZER_COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL_150'));
One is going to run in compatibility level 140, the other in 150, as foretold by ancient alien prophecy.
The two query plans will have a bit in common, but…
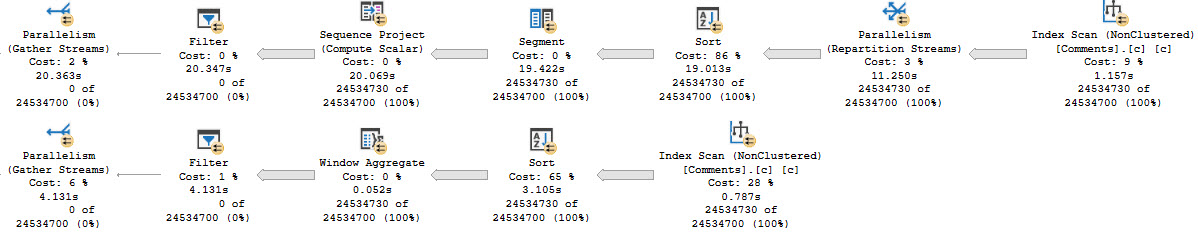
The second query, which runs in batch mode, runs about 15 seconds faster. One big reason why is that we skip that most unfortunate repartition streams operator.
It’s a cold sore. An actual factual cold sore.
The only ways I’ve found to fix it completely are:
- Induce batch mode
- Use the parallel apply technique
But the parallel apply technique doesn’t help much here, because of local factors.
In this case, me generating the largest possible result set and then filtering it down to nothing at the end.
Thanks for reading!
Going Further
If this is the kind of SQL Server stuff you love learning about, you’ll love my training. I’m offering a 75% discount to my blog readers if you click from here. I’m also available for consulting if you just don’t have time for that and need to solve performance problems quickly.
Related Posts
- Multiple Distinct Aggregates: Still Harm Performance Without Batch Mode In SQL Server
- Annoyances When Indexing For Windowing Functions In SQL Server
- Getting The Top Value Per Group With Multiple Conditions In SQL Server: Row Number vs. Cross Apply With MAX
- Getting The Top Value Per Group In SQL Server: Row Number vs. Cross Apply Performance